What Is Quantum Computing? Explained in 60 Seconds
Understand the basics of quantum computing in just one minute—with simple terms and real-world examples.

Quantum computing sounds complex—and it is. But the core idea is surprisingly simple. At its heart, quantum computing is about solving certain problems faster than regular computers. Instead of using standard bits (0s and 1s), it uses quantum bits—called qubits—that behave in unique ways.
This guide breaks down what quantum computing is, how it works, and why it matters. In 60 seconds, you’ll walk away with a basic understanding of this groundbreaking tech.
What Is Quantum Computing?
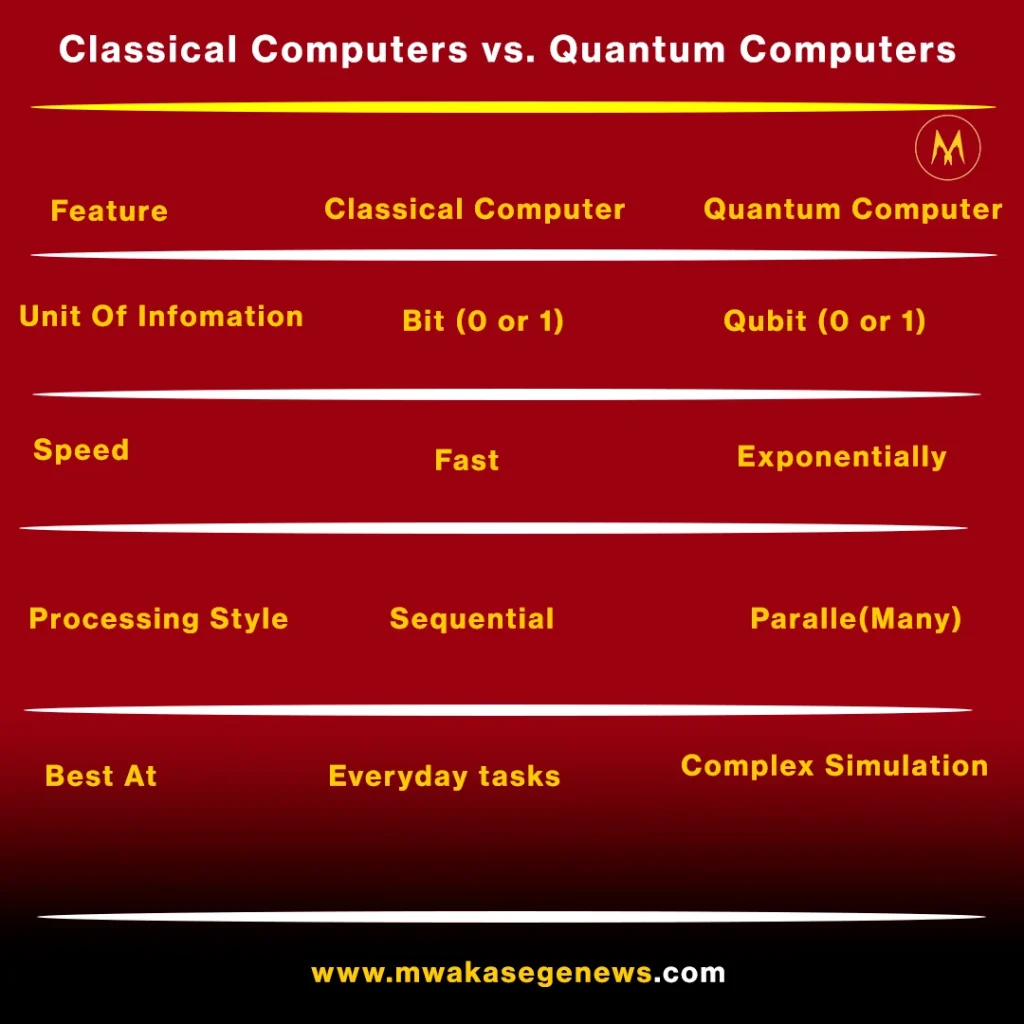
Traditional computers process information using bits, which represent either a 0 or a 1. Quantum computers use qubits, which can represent both 0 and 1 at the same time through a property called superposition.
This allows quantum computers to process a vast number of possibilities simultaneously. Another quantum property, entanglement, links qubits together in ways that increase their computing power even more.
In short, quantum computers don’t just do things faster—they do them differently.
How Does It Work in Simple Terms?
Imagine flipping a coin. A classical bit is like a coin that’s either heads (0) or tails (1). A qubit is like a spinning coin in the air—until you catch it, it’s both heads and tails at the same time. That’s superposition.
Now, take two spinning coins that always land the same way when caught, no matter how far apart they are. That’s entanglement. These unique traits allow quantum computers to explore more solutions in less time.
ALSO READ: Top 7 Tech Gadgets You Didn’t Know You Needed!
Why Is Quantum Computing Important?
Quantum computing isn’t just a cool concept—it’s a game-changer. It could revolutionize fields like:
- Cryptography: Cracking codes faster than any current system.
- Medicine: Simulating molecules to discover new drugs.
- Climate Science: Modeling complex weather systems more accurately.
- Finance: Optimizing investment strategies.
Problems that would take supercomputers thousands of years could be solved in hours with quantum computing.
Classical Computers vs. Quantum Computers
Limitations of Quantum Computing
Quantum computing isn’t ready for your smartphone yet. There are challenges like:
- Fragility of Qubits: They’re highly sensitive to environment.
- Error Rates: Calculations can be unstable without corrections.
- High Costs: Machines require extreme conditions to function.
But researchers are solving these problems step by step.
Who Is Building Quantum Computers?
Big tech and startups are in the race. Some key players include:
- IBM
- Microsoft
- Rigetti
- D-Wave
Governments and universities are also heavily investing in this future-forward field.
Will Quantum Computers Replace Classical Ones?
No. At least not completely. Classical computers will still handle everyday tasks. Quantum computers will specialize in problems too complex for regular machines. Think of them as complementary tools, not competitors.
The Future of Quantum Computing
We’re still in the early stages—what experts call the NISQ era (Noisy Intermediate-Scale Quantum). These machines aren’t perfect, but they prove the concept works. In 10–20 years, we may see practical, large-scale quantum computing changing how industries operate.
Final Thoughts
Quantum computing might sound like science fiction, but it’s very real. While it’s still developing, its potential to transform science, industry, and daily life is massive.
ALSO READ: AI Tools That Will Blow Your Mind in 2025
Understanding the basics now puts you ahead of the curve. The next time someone brings up quantum computing, you won’t be left in the dark—you’ll be the one explaining it.
FAQs
A qubit is the basic unit of quantum information. Unlike a normal bit, it can be in multiple states at once—thanks to quantum physics.
Not exactly. They need special algorithms. Classical software doesn’t work the same way on quantum machines.
Speed varies, but quantum computers can solve certain problems millions of times faster than classical ones.
Some exist today for research and development. Public access is limited, but companies like IBM offer cloud-based quantum systems.




